3.1.2. Process Creation¶
At system boot time, one user level process is created. In Unix, this process is called init. In Windows, it is the System Idle Process. This process is the parent or grand-parent of all other processes.
New Child Processes are created by another process (the Parent Process).
3.1.2.1. Windows Process Creation¶
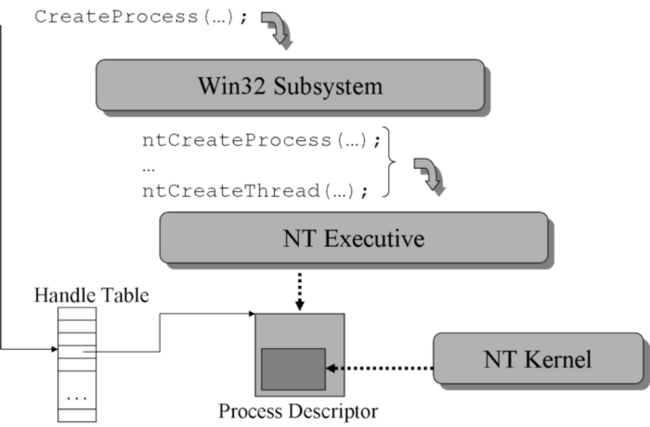
Windows process creation specifies a new program to run when the process is created.
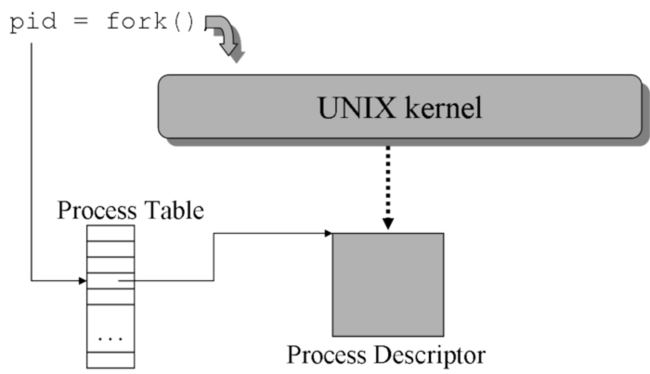
3.1.2.2. Unix Process Creation¶
- Unix
fork()creates a process - Creates a new address space
- Copies text, data, & stack into new adress space
- Provides child with access to open files
- Unix
Unix
exec()allows a child to run a new programUnix
wait()allows a parent to wait for a child to terminate
Note
In Unix, process creation and management uses multiple, fairly simple
system calls. This provides extra flexability. If needed, the parent
process may contain the code for the child process to run, so that
exec() is not always needed. The child may also set up
inter-process communication with the parent, such as with a pipe before
running another program.
The only difference between the parent and process after the call to
fork() is the return value from fork().
int pidValue;
...
pidValue = fork(); /* Creates a child process */
if(pidValue == 0) {
/* pidValue is 0 for child, nonzero for parent */
/* The child executes this code concurrently with parent */
childsPlay(...); /* A procedure linked into a.out */
exit(0);
}
/* The parent executes this code concurrently with child */
parentsWork(...);
wait(...);
...
3.1.2.3. Example: Printing using a pipe to the child process¶
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXLINE 150
#define true 1
#define false 0
int ReadLine(char *,int ,FILE *);
int main(void)
{
char *process="/usr/local/bin/lpr"; /* process to exec */
char *option="-Php126";
char line[MAXLINE];
int fd[2]; /* pipe file desc. */
FILE *fp;
pipe(fd);
if( fork() == 0 ) {/* child */
close(fd[1]);
close(0);
dup(fd[0]); /* redirect stdin to be from pipe */
close(fd[0]);
execl( process, process, option, 0 );
} else { /* parent */
close(fd[0]);
close(1);
dup(fd[1]);
close(fd[1]); /* redirect stdout to be to pipe */
fp = stdin;
while( ReadLine(line,MAXLINE,fp) ) {
printf( "%s\n", line );
}
}
return 0;
}
int ReadLine(char *buff,int size,FILE *fp)
{
buff[0] = '\0';
buff[size - 1] = '\0'; /* mark end of buffer */
if (fgets(buff, size, fp) == NULL) {
*buff = '\0'; /* EOF */
return false;
}
else {
char *tmp;
/* remove newline */
if ((tmp = strrchr(buff, '\n')) != NULL) {
*tmp = '\0';
}
}
return true;
}
