4.1.1. Handling Signals¶
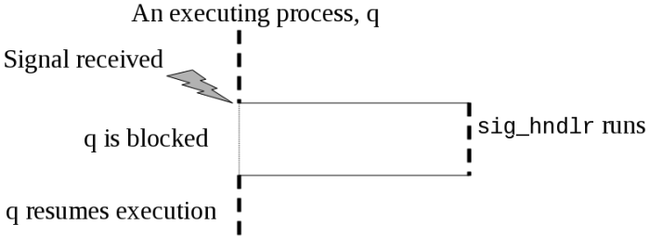
Signals other that SIG_KILL and SIG_STOP may be caught and execute a defined signal handler function.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
static void sig_handler(int);
int main ()
{
int i, parent_pid, child_pid, status;
if(signal(SIGUSR1, sig_handler) == SIG_ERR)
printf("Parent: Unable to create handler for SIGUSR1\n");
if(signal(SIGUSR2, sig_handler) == SIG_ERR)
printf("Parent: Unable to create handler for SIGUSR2\n");
parent_pid = getpid();
if((child_pid = fork()) == 0) {
kill(parent_pid, SIGUSR1);
for (;;) pause();
}
else {
kill(child_pid, SIGUSR2);
sleep(3);
printf("Parent: Terminating child ...\n");
kill(child_pid, SIGTERM);
wait(&status);
printf("done\n");
}
}
static void sig_handler(int signo) {
switch(signo) {
case SIGUSR1: /* Incoming SIGUSR1 */
printf("Parent: Received SIGUSER1\n");
break;
case SIGUSR2: /* Incoming SIGUSR2 */
printf("Child: Received SIGUSER2\n");
break;
default: break;
}
return;
}
